Here is an Easy explanation of Ohm’s Law: Class 8 science: Chapter 9
Ohm’s law is a fundamental principle in electrical engineering and physics. It describes the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance in an electrical circuit. Simply put, Ohm’s law states that the current passing through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the two points and inversely proportional to the resistance between them. This article will explain Ohm’s law and provide examples and formulas to help you understand it better.
The formula for Ohm’s law is:
V = IR
Where V is the voltage, I is the current, and R is the resistance. This formula shows that the voltage across a conductor is directly proportional to the current flowing through it and inversely proportional to the resistance of the conductor.
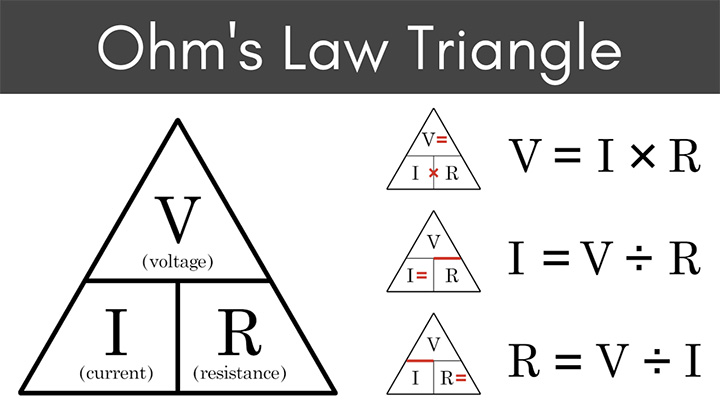
Let’s take a closer look at each of these variables:
Voltage (V) – Voltage is the electrical potential difference between two points in a circuit. It is measured in volts (V) and is typically represented by the symbol V. Voltage can be thought of as the force that drives the flow of electrons through a circuit.
Current (I) – Current is the flow of electrons through a conductor. It is measured in amperes (A) and is typically represented by the symbol I. Current can be thought of as the rate at which electrons flow through a circuit.
Resistance (R) – Resistance is the measure of how difficult it is for electrons to flow through a conductor. It is measured in ohms (Ω) and is typically represented by the symbol R. Resistance can be thought of as the “opposition” to the flow of electrons in a circuit.
Examples of Ohm’s Law in Action
Let’s look at a few examples of Ohm’s law in action to better understand how it works:
Example 1: If a circuit has a voltage of 12 volts and a resistance of 4 ohms, what is the current flowing through the circuit?
Using Ohm’s law, we can rearrange the formula to solve for I:
I = V / R
Plugging in the values, we get:
I = 12 / 4 I = 3 amps
Therefore, the current flowing through the circuit is 3 amps.
Example 2: If a circuit has a current of 5 amps and a resistance of 10 ohms, what is the voltage across the circuit?
Using Ohm’s law, we can rearrange the formula to solve for V:
V = IR
Plugging in the values, we get:
V = 5 x 10 V = 50 volts
Therefore, the voltage across the circuit is 50 volts.
Ohm’s law is a fundamental principle in electrical engineering and physics. It describes the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance in an electrical circuit. Understanding Ohm’s law is crucial for anyone working with electricity or electronics. By using the formula V = IR, you can calculate the voltage, current, or resistance in a circuit, which is essential for designing, troubleshooting, and repairing electrical systems.
Easy explanation of Ohm’s Law: Class 8 science: Chapter 9
Short Description on Photosynthesis for Class 8
Heat energy conversion in chemical reactions : Class 8 Science
Displacement Reaction: Class 8 Science : Chapter 8
অষ্টম শ্রেণির বিজ্ঞান : প্রথম তিন অধ্যায়ের সংক্ষিপ্ত প্রশ্নোত্তর
অষ্টম শ্রেণির বিজ্ঞানের একাদশ অধ্যায় : চোখের প্রধান অংশ ও কাজ
অষ্টম শ্রেণির বিজ্ঞান প্রশ্নোত্তর : অধ্যায় ১৪ : পরিবেশ এবং বাস্তুতন্ত্র
অষ্টম শ্রেণির বিজ্ঞান প্রশ্নোত্তর : অধ্যায় ১৩ : খাদ্য ও পুষ্টি
অষ্টম শ্রেণির বিজ্ঞান প্রশ্নোত্তর : অধ্যায় ১২ : মহাকাশ ও উপগ্রহ
অষ্টম শ্রেণির বিজ্ঞান প্রশ্নোত্তর : অধ্যায় ১১ : আলো
অষ্টম শ্রেণির বিজ্ঞান প্রশ্নোত্তর : দশম অধ্যায় : অম্ল, ক্ষারক ও লবণ
অষ্টম শ্রেণির বিজ্ঞান প্রশ্নোত্তর : নবম অধ্যায় : বর্তনী ও চলবিদ্যুৎ
অষ্টম শ্রেণির বিজ্ঞান প্রশ্নোত্তর অষ্টম অধ্যায় রাসায়নিক বিক্রিয়া
অষ্টম শ্রেণির বিজ্ঞান প্রশ্নোত্তর সপ্তম অধ্যায় পৃথিবী ও মহাকর্ষ
অষ্টম শ্রেণির বিজ্ঞান প্রশ্নোত্তর ষষ্ঠ অধ্যায় পরমাণুর গঠন
অষ্টম শ্রেণির বিজ্ঞান প্রশ্নোত্তর পঞ্চম অধ্যায় সমন্বয় ও নিঃসরণ
অষ্টম শ্রেণির বিজ্ঞান প্রশ্নোত্তর চতুর্থ অধ্যায় উদ্ভিদের বংশবৃদ্ধি
অষ্টম শ্রেণির বিজ্ঞান : তৃতীয় অধ্যায় : ব্যাপন অভিস্রবণ ও প্রস্বেদন
অষ্টম শ্রেণির বিজ্ঞান : দ্বিতীয় অধ্যায় : জীবের বৃদ্ধি ও বংশগতি
অষ্টম শ্রেণির বিজ্ঞান : প্রথম অধ্যায় : প্রাণীজগতের শ্রেণিবিন্যাস