Introduction
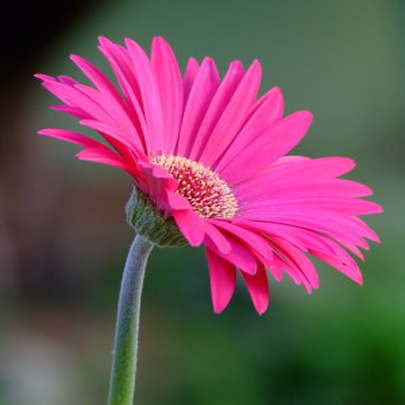
Gerbera is an important commercial flower belonging to the Asteraceae family. It was named after the German naturalist Traugott Gerber. In the international flower trade, Gerbera is one of the most popular “cut flowers” due to its bright colors and long vase life.

Varieties
There are about 40 species under the Gerbera genus. Among them, Gerbera jamesonii is the most widely cultivated. In Bangladesh, the Bangladesh Agricultural Research Institute has developed two main varieties:
- BARI Gerbera-1
- BARI Gerbera-2
Climate
Gerbera is a hardy plant. It thrives in open fields in tropical regions and in greenhouses in subtropical or temperate zones. The ideal daytime temperature is 16–20°C, while nighttime should be 10–12°C. In hot weather, a 30% shade net improves flower quality.
Soil
Well-drained, fertile loamy or sandy-loam soils are ideal. The soil pH should be between 5.5 and 7.0. Enrich the soil with organic matter such as cow dung, compost, or coco dust for best results.
Propagation
- By seeds – Easy but doesn’t maintain parent traits.
- By clump division – Mature plants are divided into small portions and replanted.
- By micropropagation – Using tissue culture for high-quality, disease-free plantlets.
Cultivation
1. Land Preparation
Till the land 2–3 times to loosen the soil to a depth of 40–45 cm. Mix in plenty of organic manure.
2. Bed Preparation
Make raised beds about 20 cm high and 1.0–1.2 meters wide. Leave 50 cm wide drainage channels between the beds.
3. Planting
Maintain a spacing of 50 cm between rows and 40 cm between plants. Make sure the plant crown stays above soil level.
4. Planting Time
October to November is the best time for planting Gerbera.
5. Irrigation
Use flood irrigation. Avoid waterlogging, as it can cause diseases. After each irrigation, loosen the topsoil with a hoe.
6. Fertilizer Application (Per Hectare)
- Cow dung/compost: 10 tons
- Coco dust: 2 tons
- Urea: 350 kg
- TSP (Triple Super Phosphate): 250 kg
- MOP (Muriate of Potash): 300 kg
- Gypsum: 165 kg
- Boric acid: 12 kg
- Zinc oxide: As required
Application Schedule:
Apply organic manure, TSP, and other base fertilizers 10–15 days before planting. Apply half of the urea 25 days after planting and the rest after 45 days, followed by irrigation.
Pest and Disease Management
Common Diseases:
- Root rot: Caused by soil-borne fungi. Use sterilized soil to prevent it.
- Crown rot: The central part of the plant rots.
- Powdery mildew: White, powdery coating on leaves.
Control Measures:
- Spray with Ridomil, Dithane M-45, or Topsin every 7–10 days.
- Use Benomyl 50 WP at 0.01% concentration.
Common Pests:
- Mites: Appear in dry, hot weather.
- Whiteflies: Suck sap and can transmit viral diseases.
Control Measures:
- Remove and burn infected leaves.
- Spray with Vertimec, Omite 57 EC, neem seed extract, or a combination of Actara 75 SP and Kumulus DF.
Flower Harvesting
Harvest when the outer two rows of disk florets are aligned with the stem. After cutting, trim the stalk diagonally and immediately place the stem in 1-inch deep water. Add a pinch of sugar and a few drops of lemon juice to prolong vase life.
Yield
Yields vary by variety, but on average, each plant produces 20–25 flowers per year.